The night sky has long been an enchanting canvas, studded with celestial wonders that have captivated humanity’s imagination for eons. Among these cosmic companions, our very own moon has held a special place in our hearts. Its beauty and mysteries have been explored and celebrated throughout history. But the universe is vast, and our moon is just one of many fascinating worlds orbiting distant planets. In this blog, we invite you on a celestial journey to discover “6 Moons Beyond Earth: A Tour of Planets with Moon Companions.”
These moons, each with its own unique characteristics, beckon us to explore their enigmatic landscapes, hidden oceans, and breathtaking phenomena. From the volcanic eruptions of Io to the icy mysteries of Europa, the methane lakes of Titan, the geysers of Enceladus, and the retrograde orbit of Triton, each moon unveils a story that leaves us in awe of the cosmic diversity that surrounds us.
Join us as we embark on this interplanetary adventure, unraveling the secrets and wonders of these extraordinary moons beyond Earth’s gentle embrace.
Moons Beyond Earth
Discover the hidden wonders of celestial companions in our solar system as we embark on a cosmic odyssey to unveil the secrets of Moons Beyond Earth.
1. Earth
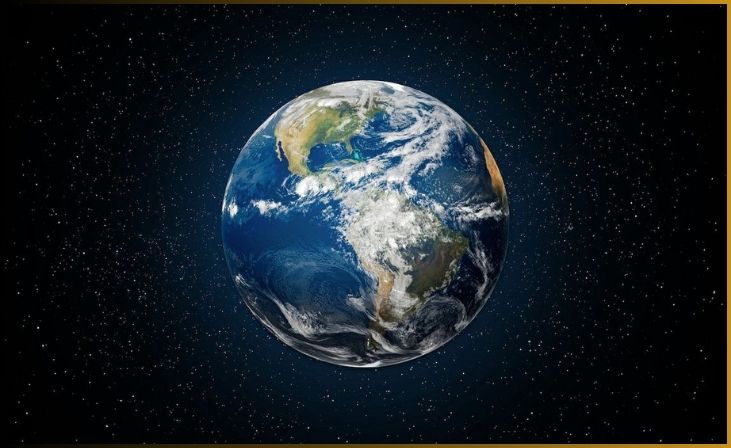

Earth, often referred to as the “Blue Planet,” is the third planet from the sun in our solar system. It is the only celestial body known to support life, making it an oasis of incredible diversity and beauty in the vast cosmos. Earth’s unique characteristics make it a remarkable world. It possesses a dynamic atmosphere that sustains a complex web of life, including an array of ecosystems and a rich diversity of species.
Earth’s surface is predominantly covered by oceans, which play a pivotal role in regulating the planet’s climate and providing habitat for a multitude of marine life forms. The land, with its varied landscapes, hosts everything from towering mountain ranges to lush forests, vast deserts, and fertile plains.
Our planet is also distinguished by its moon, which, as Earth’s only natural satellite, has shaped our history, culture, and even our understanding of the cosmos. Earth’s geological features, including tectonic plate movements, volcanoes, and erosion, have created a constantly changing landscape that continues to be explored and studied by scientists.
For More- 7 Time-Tested Jobs That Will Always Be in Demand
2. Mars
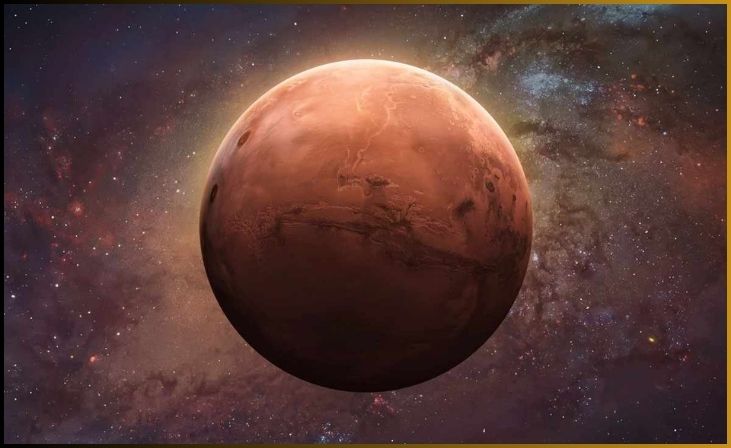

Mars, often referred to as the “Red Planet,” is the fourth planet from the sun in our solar system. It has long held a special place in our collective imagination as one of the most Earth-like planets, making it a subject of fascination and exploration. Mars is characterized by its rusty-red color, which is attributed to the presence of iron oxide, or rust, on its surface.
Mars is a terrestrial planet with a landscape that includes vast deserts, towering volcanoes, deep canyons, and a polar ice cap. One of its most distinctive features is Olympus Mons, the largest volcano in the solar system. Additionally, Mars has a thin atmosphere primarily composed of carbon dioxide, which is inhospitable to human life, but it plays a vital role in the planet’s weather and climate.
The planet has been a primary focus of exploration due to its potential to harbor life or provide insights into past life. Numerous missions, including rovers like Curiosity and Perseverance, have been sent to study its surface and search for signs of water and ancient life. Mars also serves as a possible candidate for future human colonization, making it a key subject of scientific research and space exploration in our quest to understand the potential for life beyond Earth.
3. Jupiter
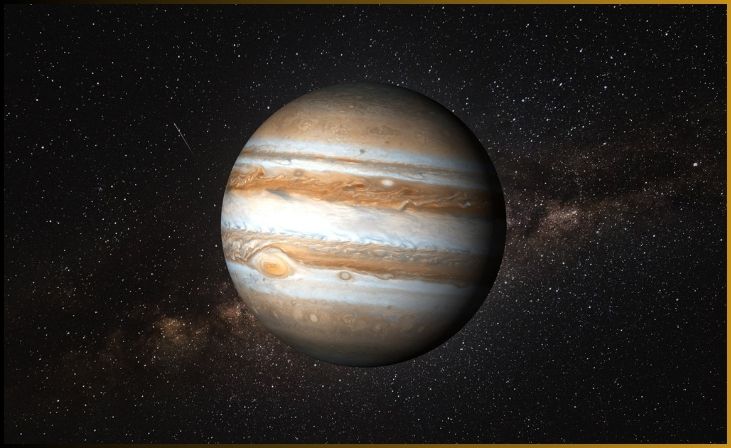

Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, is a true behemoth that reigns as the fifth planet from the sun. Its colossal size is a defining feature, as it could easily contain all the other planets within its voluminous girth and still have room to spare. This gas giant’s most prominent feature is its swirling bands of clouds and its iconic Great Red Spot, a massive storm that has raged for centuries.
Jupiter’s atmosphere is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, and its intense gravitational pull is responsible for shaping the orbits of numerous celestial bodies in the solar system. Jupiter’s system of over 80 moons includes some of the largest in the solar system, such as Ganymede, Callisto, and Europa, which are intriguing targets for exploration due to the possibility of subsurface oceans and potential habitability.
4. Saturn
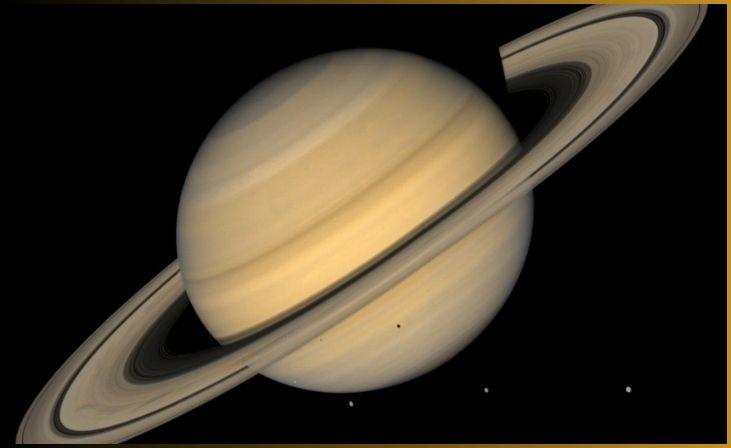
Saturn, the sixth planet from the sun in our solar system, is often celebrated as the “Ringed Giant” due to its magnificent system of rings that encircle it. These dazzling rings are composed of countless particles of ice and rock, creating a breathtaking and otherworldly spectacle in the night sky. Saturn’s rings are not only a visual wonder but also a testament to the intricate dynamics of celestial bodies.
Beneath its distinctive rings, Saturn is a gas giant, primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, similar to its neighboring planet Jupiter. It’s the second-largest planet in our solar system, known for its striking bands of clouds and the presence of massive storms, including the hexagonal storm at its north pole.
Saturn’s family of moons, numbering over 80, includes the moon Titan, which stands out as one of the most fascinating. Titan possesses a thick atmosphere and has been a target of exploration due to its potential for prebiotic chemistry and Earth-like features.
5. Uranus
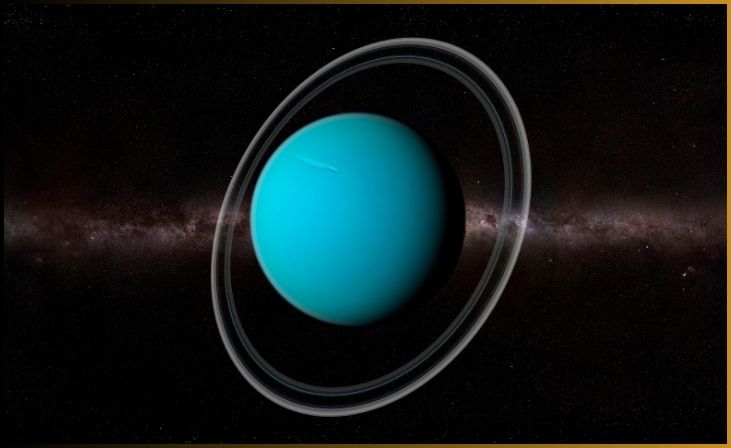
Uranus, the seventh planet from the sun, is a unique and enigmatic world in our solar system. Unlike most of its planetary neighbors, Uranus rotates on its side, making it appear as if it’s rolling along its orbital path. This axial tilt, along with its pale blue-green hue, sets it apart from the other gas giants.
Uranus is an ice giant, primarily composed of water, ammonia, and methane ices. Its atmosphere is marked by a mix of hydrogen and helium, much like Jupiter and Saturn. Its most distinctive feature is the presence of faint, narrow rings and a diverse family of moons.
One of the most intriguing moons of Uranus is Miranda, which boasts some of the most diverse landscapes in the solar system, including towering cliffs and strange, jumbled terrain. These features have led scientists to theorize about the moon’s turbulent past.
6. Neptune
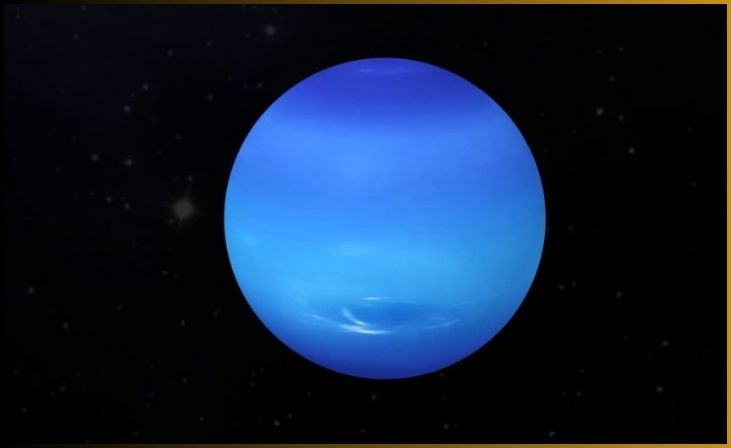

Neptune, the eighth and farthest known planet from the sun, is a distant and mysterious world in our solar system. Named after the Roman god of the sea, Neptune’s deep blue appearance is aptly fitting, given its icy and turbulent atmosphere. It’s often referred to as an “ice giant,” similar to Uranus, due to its primarily water, ammonia, and methane composition.
Neptune’s atmosphere is characterized by extreme weather patterns, including the fastest winds in the solar system, which can reach speeds of over 1,000 miles per hour. One of the most prominent features of Neptune is the Great Dark Spot, a massive storm system that comes and goes in its turbulent atmosphere.
Neptune is orbited by a diverse family of moons, the most notable of which is Triton. Triton is unique in that it orbits Neptune in a retrograde direction, opposite to the planet’s rotation, and it’s believed to be a captured Kuiper Belt object. Triton’s surface is marked by geysers of nitrogen gas, making it one of the coldest known places in the solar system.
Also Read- Old-School Etiquette Rules That Have Disappeared
Interesting facts about the Moon
Certainly, the Moon is a celestial body filled with fascinating facts. Here are some interesting ones:
- Ancient Lunar Impact Basins: The Moon’s surface is pockmarked with impact craters, the largest of which are called basins. Some of these basins, like the South Pole-Aitken Basin, are so old they date back over 4 billion years, providing a glimpse into the early history of our solar system.
- Earth’s Tidal Lock: The Moon is tidally locked to Earth, meaning it always shows the same face to us. This lock is the result of gravitational interactions, and it’s not unique; many moons in our solar system are tidally locked to their host planets.
- Lunar Maria: The dark, flat plains on the Moon are called lunar maria (singular: mare), which means “seas” in Latin. However, they are not actually seas but vast solidified lava plains resulting from volcanic activity billions of years ago.
- Cold and Hot Extremes: While the Moon’s surface can reach scorching temperatures of over 250 degrees Fahrenheit (120 degrees Celsius) during the lunar day, it plunges to around -250 degrees Fahrenheit (-157 degrees Celsius) during the frigid lunar night due to the lack of a protective atmosphere.
- Footprints Remain Forever: There is no erosion or weathering on the Moon, so the footprints and tire tracks left by astronauts during the Apollo missions in the late 1960s and early 1970s are still there, perfectly preserved.
- Moonquakes: The Moon experiences moonquakes, which are caused by the gravitational interactions with Earth and the cooling and contracting of the lunar interior. They are not as intense as Earthquakes but can last longer.
- Lunar Regolith: The Moon’s surface is covered in a layer of fine dust and rock fragments known as lunar regolith. This layer can be very abrasive and cling to astronaut suits, potentially causing equipment damage.
Conclusion
In our cosmic journey exploring “Moons Beyond Earth: A Tour of Planets with Moon Companions,” we’ve ventured into a captivating realm where celestial bodies unveil their unique stories. From the Earth’s familiar moon to the volcanic tumult of Io, the hidden oceans of Europa, the methane lakes of Titan, the geysers of Enceladus, and the retrograde orbit of Triton, each moon carries its own enigmatic charm and intrigue.
These moons are not just distant neighbors but gateways to understanding the broader universe. They offer us invaluable insights into planetary formation, the potential for extraterrestrial life, and the dynamic forces that shape the cosmos. As we gaze upon these cosmic companions, we’re reminded of the boundless wonder of our solar system.
The universe continues to beckon us with its mysteries, and as we look to the skies, these moons, each with its own unique story, remain a testament to the awe-inspiring diversity that surrounds us.
FAQs
Yes, several upcoming missions are planned to explore these moons further, including the Europa Clipper mission and proposed missions to Enceladus, Titan, and Triton.
Conditions vary significantly from moon to moon. Some have harsh, airless environments, while others may have thin atmospheres or subsurface oceans. None of them offer conditions suitable for human life without significant adaptation.
Moons like Europa and Enceladus, with their subsurface oceans, are of particular interest as potential habitats for life beyond Earth. Their study is crucial to understanding the possibility of life elsewhere in the solar system.
While some moons have resources that could be used for future space missions, the challenges of colonization, such as extreme cold, lack of atmosphere, and distance from Earth, make them difficult candidates for human habitation.
Recent discoveries, such as water ice on the Moon and subsurface oceans on Europa, have advanced our understanding of these celestial bodies and their significance in planetary science, astrobiology, and space exploration.

