The natural world is teeming with diverse and fascinating life forms, each with its own unique survival strategies. Among these, there are creatures that stand out for their remarkable ability to reproduce at astonishing rates. In this blog, we embark on a journey to explore the planet’s fastest-reproducing animals, shedding light on the captivating reproductive prowess that has allowed them to thrive in their respective environments.
From the prolific breeding of rabbits, whose populations can skyrocket under the right conditions, to the tiny but mighty fruit flies that have unlocked secrets of genetics through their swift generations, these animals offer a glimpse into the extraordinary world of life’s resilience. We delve into the worlds of bacteria, house mice, and aphids, where reproduction is a race against time, and learn about the fascinating adaptations of cockroaches, nematode worms, and the enigmatic Mexican Walking Fish.
Through these tales of rapid multiplication, we uncover the astonishing ways in which life adapts, perseveres, and continues to thrive in the ever-changing tapestry of our planet.
Fastest-Reproducing Animals
Here are the World’s Reproductive Champions: Meet nature’s most prolific parents as we unveil the top contenders in the race for rapid reproduction, showcasing their astonishing strategies and remarkable life cycles.
1. Rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus)

Rabbits, scientifically known as Oryctolagus cuniculus, are renowned for their remarkable reproductive capabilities. These small mammals are prolific breeders, and their reproductive system is finely tuned for rapid population growth. A single pair of rabbits can give birth to multiple litters in a single year, and each litter typically contains several kits. The speed at which they reproduce is truly remarkable. Under ideal conditions, a pair of rabbits can potentially produce more than 30 offspring in a single year.
Their ability to breed so rapidly is a result of several factors, including a short gestation period, early sexual maturity, and the capacity to conceive again shortly after giving birth. This remarkable reproductive strategy ensures that rabbits have a strong presence in various ecosystems, but it also highlights their vulnerability to population fluctuations in the wild and their status as both prey and pest in different environments.
Also Read- Top 15 Pet Animals for Kids at Each Age
2. House Mice (Mus musculus)
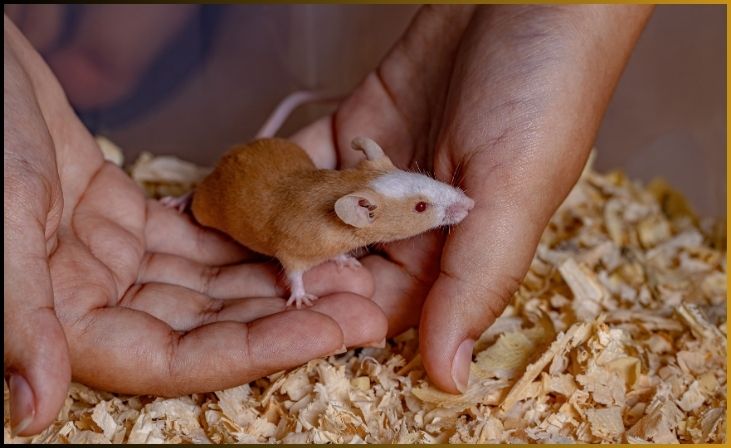

House mice, scientifically known as Mus musculus, are among the world’s most prolific rodents when it comes to reproduction. These small creatures are highly adaptable and have evolved to thrive in a variety of environments, often in close proximity to human settlements. What sets them apart is their extraordinary reproductive rate. A single female house mouse is capable of producing multiple litters of pups throughout the year, with each litter containing several offspring.
Their ability to reproduce rapidly is due to several factors, including a short gestation period, typically around three weeks, and a relatively quick maturation to sexual maturity, often occurring at just a few weeks of age. In favorable conditions, a pair of house mice can give rise to a burgeoning population within a short period. This high reproductive potential has made them successful colonizers and, at the same time, formidable pests in agriculture and households worldwide, requiring effective control measures to manage their populations.
3. Fruit Flies (Drosophila melanogaster)
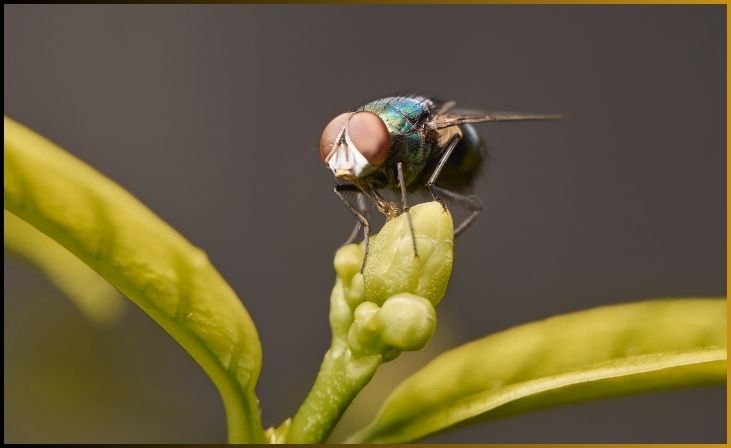

Fruit flies, scientifically known as Drosophila melanogaster, are tiny insects celebrated for their extraordinary reproductive capacity and their significant role in genetic research. These insects have a short life cycle and a rapid reproductive rate, making them a valuable model organism in scientific laboratories. A single fruit fly can complete its entire life cycle, from egg to adult, in as little as 10 days under optimal conditions.
This accelerated life cycle is a boon for genetic studies because it allows researchers to observe multiple generations in a relatively short time, making it easier to study inheritance patterns and genetic mutations. Fruit flies have been instrumental in unraveling the fundamental principles of genetics and the genetic basis of various traits. Their prolific reproduction and rapid development continue to provide insights into genetics, development, and evolution, making them an indispensable tool for scientific inquiry.
4. Bacteria (Various species)
Bacteria, representing a vast and diverse group of microorganisms encompassing various species, are among the fastest-reproducing life forms on Earth. These microscopic entities multiply at an astonishing pace, demonstrating their remarkable adaptability and resilience. Under optimal conditions, some bacterial species can divide and reproduce every 20 minutes, giving rise to exponential population growth. Their rapid reproduction is driven by binary fission, a process in which one bacterium splits into two identical daughter cells.
This capacity for swift replication is a fundamental characteristic of bacteria and a key factor in their success as a life form. However, this extraordinary reproductive rate is not without consequences, as it can lead to issues such as the rapid development of antibiotic resistance, the initiation of infectious diseases, and their significant impact on various ecosystems. Bacteria’s rapid reproductive abilities underscore their critical role in Earth’s ecosystems and various aspects of human life, from health to biotechnology.
5. Aphids (Aphidoidea)
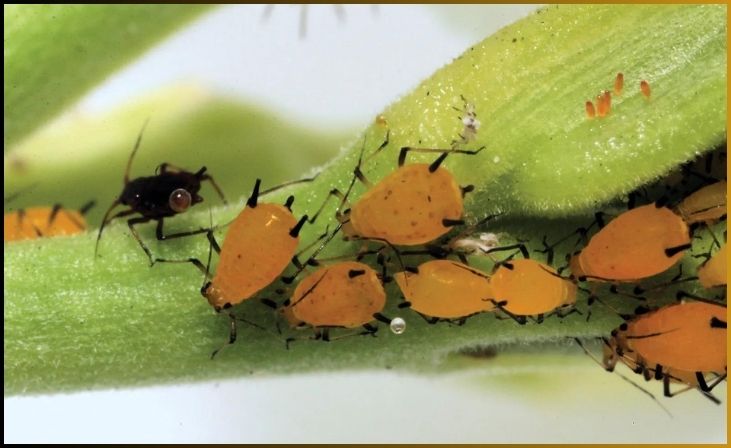

Aphids, belonging to the family Aphidoidea, are small, sap-sucking insects known for their remarkable ability to reproduce rapidly and their unique reproductive strategy. These insects have adapted to a lifestyle that promotes quick population growth. One of their most striking features is asexual reproduction, allowing many aphid species to produce live offspring without the need for mating. This means that a single aphid, often a female, can give birth to numerous genetically identical daughters in rapid succession.
Under favorable environmental conditions, an aphid population can explode within a short time frame. The ability to reproduce parthenogenetically, without the need for males, is a fascinating adaptation that ensures the rapid colonization of plants and, at the same time, challenges agricultural and horticultural efforts. Aphids’ remarkable reproductive abilities have made them a subject of interest in ecology, agriculture, and entomology due to their impact on crop plants and the intricate interactions they have with their environment.
6. Cockroaches (Various species)

Cockroaches, found in various species worldwide, are renowned for their remarkable reproductive resilience. These insects have adapted to thrive in a wide range of environments, thanks in part to their impressive reproductive abilities. Some species of cockroaches have evolved to reproduce quickly, and this adaptation is essential for their survival. Female cockroaches can produce multiple egg cases, or oothecae, over their lifetimes, and each of these oothecae can contain numerous eggs.
The eggs hatch into nymphs, which then mature into adult cockroaches. This cycle repeats, often with a short incubation period between generations, leading to rapid population growth. Cockroaches’ ability to reproduce prolifically is a key reason they have become such successful survivors over millions of years, even in the face of changing environments and human efforts to control them. Their resilience and high reproductive rates can pose challenges when dealing with pest control, as they can quickly reestablish infestations in favorable conditions.
7. Nematode Worms (Caenorhabditis elegans)
Nematode worms, with Caenorhabditis elegans being a prominent example, are small, unsegmented roundworms that have garnered significant attention in scientific research due to their unique characteristics, including their fast reproductive rate. These microscopic worms have short life cycles, typically lasting just a few days, and can reproduce rapidly under laboratory conditions. Each hermaphroditic nematode worm can produce self-fertilized eggs, ensuring a swift generation turnover. This high reproductive rate has made C. elegans an invaluable model organism in biological and genetic research.
Scientists have utilized this worm to explore fundamental biological processes, study genetic mutations, and investigate neurobiology, development, and aging. Its relatively simple and well-understood biology, coupled with its remarkable ability to reproduce quickly, has elevated the nematode worm to a critical role in advancing our understanding of complex biological phenomena. This model organism’s contribution to various fields of science underscores the significance of rapid reproduction in enabling in-depth investigations and experiments.
Click Here- The World’s Longest-Living Animals: A Fascinating Exploration
8. Mexican Walking Fish (Axolotl) (Ambystoma mexicanum)
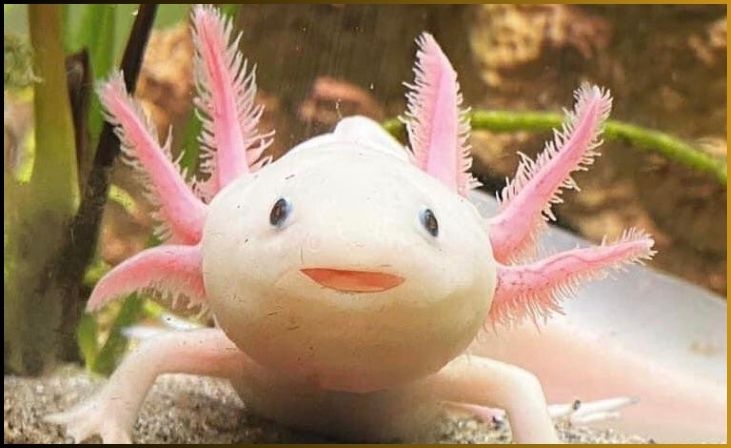

The Mexican Walking Fish, scientifically known as Ambystoma mexicanum, is a captivating amphibian renowned for its remarkable reproductive capabilities and unique regenerative abilities. Native to the ancient water systems of Mexico, axolotls remain in their aquatic larval form throughout their lives, a feature called neoteny. This species can lay an astonishing number of eggs, with a single reproductive event producing hundreds or even thousands of eggs. Axolotls’ reproduction is noteworthy not only for the sheer quantity of offspring they can produce but also for their exceptional regenerative abilities.
These creatures have the remarkable capability to regrow lost body parts, including limbs, spinal cord, and even parts of the heart. This regenerative power, coupled with their prolific reproduction, makes them a subject of extensive scientific research aimed at understanding the potential applications for human tissue regeneration. The Mexican Walking Fish’s combination of rapid reproduction and regenerative abilities showcases a unique and intriguing facet of the animal kingdom, making them both a scientific marvel and a conservation concern in their native habitat.
Effects of Some Environmental Factors on the Reproduction
The reproduction of animals is profoundly influenced by various environmental factors, which can either facilitate or hinder the process. These factors play a crucial role in determining the success of a species in its specific habitat. Here are some key effects of environmental factors on reproduction:
- Temperature and Climate: Temperature has a significant impact on the reproductive behaviors and rates of many animals. Some species are adapted to specific temperature ranges for breeding, and changes in climate can disrupt these patterns. For instance, sea turtles rely on temperature-dependent sex determination, which makes them vulnerable to climate change.
- Food Availability: Adequate nutrition is essential for reproduction. A shortage of food can lead to delayed breeding, reduced fertility, or even failure to reproduce. Conversely, plentiful food resources can lead to increased reproductive rates.
- Habitat Quality: The quality and availability of suitable habitats affect an animal’s decision to breed and raise offspring. Habitat destruction or degradation can lead to reduced reproductive success.
- Predator-Prey Dynamics: The presence and behavior of predators can influence an animal’s reproductive strategies. For prey species, high predation rates can result in a need for rapid reproduction to offset losses.
- Seasonal Factors: Many animals have evolved to breed during specific seasons when conditions are most favorable for offspring survival. Seasonal changes in day length, temperature, and food availability trigger these reproductive events.
- Migration Patterns: For migratory species, environmental cues like temperature and food availability at breeding and wintering sites play a crucial role in determining when and where they reproduce.
- Human Activity: Human actions, such as habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change, can disrupt environmental factors and have significant consequences on animal reproduction. Pollution, for example, can affect hormone levels and reproductive health.
More Info- Discover 12 Smells That Snakes Absolutely Hate
Conclusion
In the world of nature, speed is often synonymous with survival, and the ability to reproduce quickly is a remarkable adaptation. The eight fastest-reproducing animals we’ve explored in this blog exhibit an incredible array of reproductive strategies, from prolific breeding to asexual reproduction and swift life cycles. These adaptations enable them to flourish in various environments, both as remarkable examples of biological resilience and, at times, as formidable challenges to human interests.
FAQs
Yes, there can be downsides. Rapid reproduction can lead to overpopulation, resource depletion, and competition for space and food. In some cases, these animals can become pests, posing challenges for agriculture and ecosystems.
No, not all species within these animal groups reproduce rapidly. There is variation even within the same genus or family, and the reproductive rate can be influenced by environmental conditions and other factors.
Yes, some of these animals may face conservation challenges due to overexploitation, habitat destruction, or invasive species. Understanding their reproductive patterns is important for conservation efforts.
Studying these animals provides insights into genetics, ecology, and evolutionary biology. They are valuable for scientific research and help us understand the mechanisms that underlie rapid reproduction and population dynamics.
In some cases, population control measures are used to manage rapid reproducers, especially when they become pests. These may include biological, chemical, or cultural control methods.

